Page 300 - Bank-Muamalat_Annual-Report-2023
P. 300
BANK MUAMALAT MALAYSIA BERHAD
NOTES TO THE
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
31 DECEMBER 2023 (18 JAMADIL AKHIR 1445H)
47. FINANCIAL RISK MANAGEMENT OBJECTIVES AND POLICIES (CONT’D.)
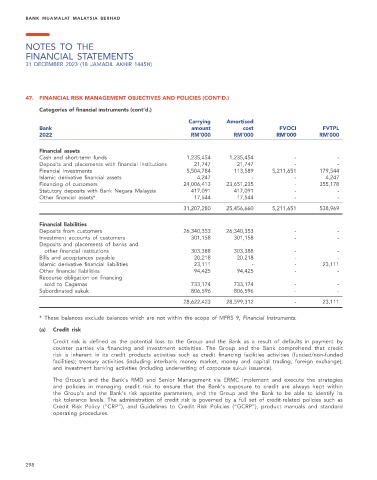
Categories of financial instruments (cont’d.)
Carrying Amortised
Bank amount cost FVOCI FVTPL
2022 RM’000 RM’000 RM’000 RM’000
Financial assets
Cash and short-term funds 1,235,454 1,235,454 - -
Deposits and placements with financial institutions 21,747 21,747 - -
Financial investments 5,504,784 113,589 5,211,651 179,544
Islamic derivative financial assets 4,247 - - 4,247
Financing of customers 24,006,413 23,651,235 - 355,178
Statutory deposits with Bank Negara Malaysia 417,091 417,091 - -
Other financial assets* 17,544 17,544 - -
31,207,280 25,456,660 5,211,651 538,969
Financial liabilities
Deposits from customers 26,340,353 26,340,353 - -
Investment accounts of customers 301,158 301,158 - -
Deposits and placements of banks and
other financial institutions 303,388 303,388 - -
Bills and acceptances payable 20,218 20,218 - -
Islamic derivative financial liabilities 23,111 - - 23,111
Other financial liabilities 94,425 94,425 - -
Recourse obligation on financing
sold to Cagamas 733,174 733,174 - -
Subordinated sukuk 806,596 806,596 - -
28,622,423 28,599,312 - 23,111
* These balances exclude balances which are not within the scope of MFRS 9, Financial Instruments.
(a) Credit risk
Credit risk is defined as the potential loss to the Group and the Bank as a result of defaults in payment by
counter parties via financing and investment activities. The Group and the Bank comprehend that credit
risk is inherent in its credit products activities such as credit financing facilities activities (funded/non-funded
facilities); treasury activities (including interbank money market, money and capital trading, foreign exchange);
and investment banking activities (including underwriting of corporate sukuk issuance).
The Group’s and the Bank’s RMD and Senior Management via ERMC implement and execute the strategies
and policies in managing credit risk to ensure that the Bank’s exposure to credit are always kept within
the Group’s and the Bank’s risk appetite parameters, and the Group and the Bank to be able to identify its
risk tolerance levels. The administration of credit risk is governed by a full set of credit-related policies such as
Credit Risk Policy (“CRP”), and Guidelines to Credit Risk Policies (“GCRP”), product manuals and standard
operating procedures.
298